Transforming Beer Foam Insights into Energy Efficiency Solutions
Written on
Chapter 1: The Overlooked Impact of Beer Foam on Energy Use
The connection between beer foam and energy consumption may seem trivial, yet it highlights how often we overlook elements that could help minimize our energy needs. This discussion focuses on achieving a lasting decrease in global greenhouse gas emissions that surpasses those produced by international shipping, independent of weather variations.
Consider the scenario of ordering a draft beer. Most draft systems utilize CO2 gas to transfer the beer from the keg to your glass, creating foam in the process. The amount of foam varies by location; some regions experience minimal foam, while others accept a frothy head as a norm. The quality of this foam is contingent upon the tuning of the dispensing system. This narrative of beer foam mirrors the efficiency challenges faced by air conditioning (AC) appliances.

Electricity and Draft Beer: A Parallel Exploration
The concept of enhancing efficiency in AC devices has been around for years. In developed nations, it is commonly adopted in industry and large enterprises, but the residential and small to medium-sized business (SMB) sectors remain largely neglected. The challenge arises from our inability to recognize broader efficiency benefits due to singular focus.
To clarify, let’s discuss the foundational elements of an AC electrical system:
- Active Power (P): This represents the effective work done by an appliance, measured in Watts (W). It’s akin to the beer you actually drink—without the foam.
- Reactive Power (Q): Measured in Volt-Amps-Reactive (VAR), this is similar to the foam in your glass, serving only a temporary or aesthetic purpose. While a small amount is necessary for the operation of AC motors, excess reactive power incurs additional costs that impact consumers, especially in less developed areas.
- Apparent Power (S): Represented in Volt-Amps (VA), this indicates what you see on your electricity bill. The apparent power is influenced by the amount of reactive power, or foam, present.
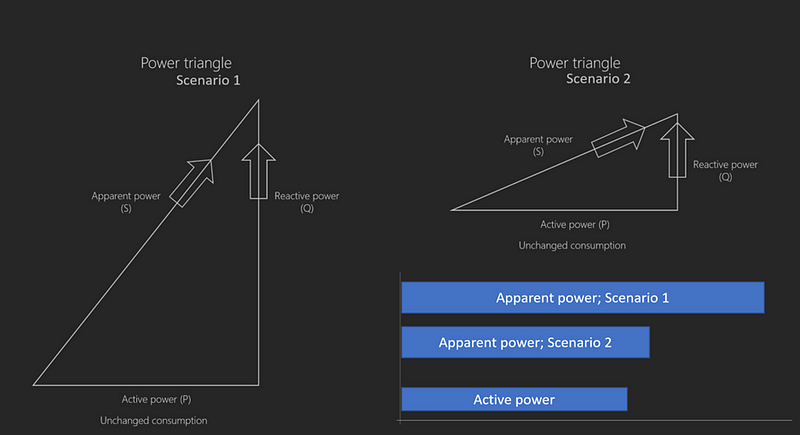
Illustrating the Concept with Washing Machines
Let’s consider two washing machines with equal active power but differing efficiencies:
- Scenario 1: Washing machine 1 consumes more reactive power (more foam), resulting in a higher apparent power reflected in your bill.
- Scenario 2: Washing machine 2 utilizes less reactive power (less foam), leading to a reduced apparent power and, consequently, a lower electricity bill.
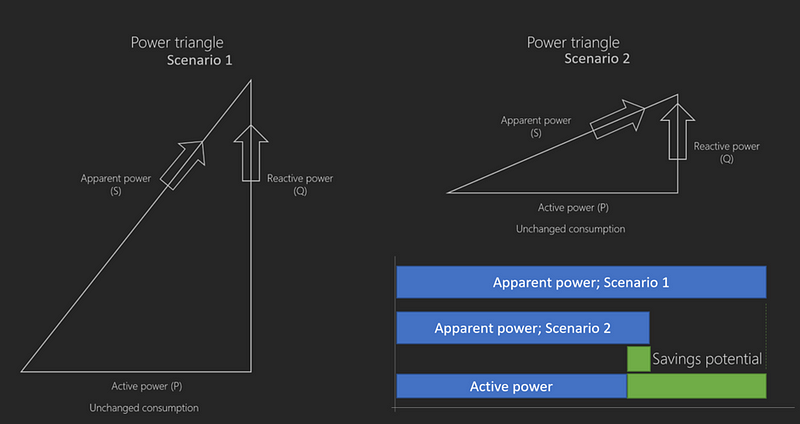
Understanding the Power Factor
The power factor (PF) is a critical measure of energy efficiency, calculated as the ratio of active power (kW) to apparent power (kVA):
PF = Active power / Apparent power
A PF closer to 1 indicates higher efficiency. While traditional incandescent bulbs typically achieve this, many LED lights fall short without integrated power factor correction technology.
The existence of reactive power significantly impacts overall energy efficiency, which is often misunderstood in energy labeling practices.
The Misconception of Energy Labels
Energy labels often focus solely on active power, disregarding reactive power and the associated costs. This approach leads to misleading assessments of appliance efficiency, as it does not factor in the complete energy picture.
As the number of AC appliances with low power factors increases, so does the unnecessary demand for energy generation, contributing to higher emissions.
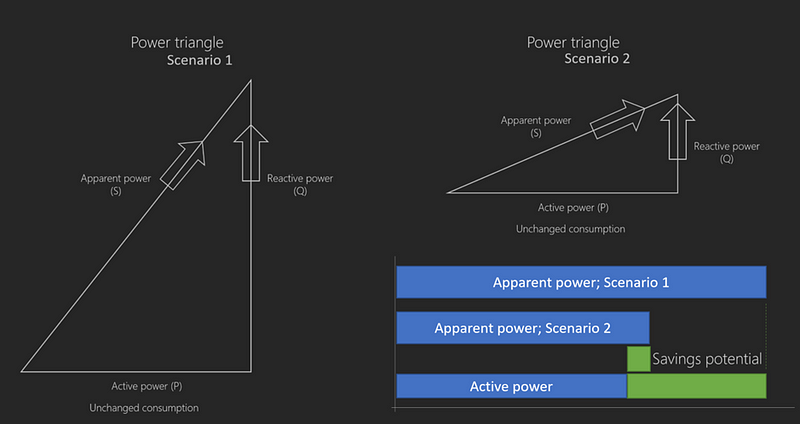
Exploring the Potential for Emission Reductions
If we could minimize the generation of reactive power, we would uncover vast potential for energy savings, directly influencing emissions reduction. Implementing power factor correction (PFC) can enhance electrical efficiency, lower utility bills, and reduce unnecessary energy production.
This creates a win-win scenario, as effective PFC measures can be applied universally, from individual homes to large enterprises.
Quick Statistics and Insights
In 2021, global electricity generation reached 28.5 PWh, with households consuming 27% of this total (7.7 PWh). A mere 30% increase in power factor could yield significant savings of up to -1.4 PWh per year in household energy consumption, translating to an 18.2% reduction globally.
If we apply these metrics to emissions, we find a potential reduction of 840 Mt CO2 annually from fossil fuel use, equating to 8.5% of the total emissions from the power industry in 2021. This is comparable to the emissions produced by Japan, the fifth-largest global polluter, or 77% of emissions from international aviation and shipping combined.
Chapter 2: Unpacking Beer Foam’s Role in Energy Efficiency
In this video, “What's Causing YOUR DRAFT SYSTEM TO POUR FOAM and HOW TO FIX IT! | MoreBeer!”, we explore how foam impacts draft beer systems and what can be done to optimize performance.
The second video, “Under the Influence of Beer Foam,” delves into the science behind beer foam and its surprising effects on energy efficiency.