# Understanding Computer Vision: Types and Applications in AI
Written on
Introduction to Computer Vision
In this article, we will delve into the concept of computer vision and explore the various models within this dynamic field of artificial intelligence (AI). Computer vision has become an integral part of numerous applications, and understanding its basics is essential for anyone interested in AI.
If you're curious about what computer vision entails and wish to learn more, continue reading. We will discuss the three primary types of computer vision models: Classification, Detection, and Segmentation. But first, let's clarify what computer vision actually is.
What is Computer Vision?
Computer vision is a specialized area of artificial intelligence that enables machines to interpret and analyze visual data—such as digital images and videos. The primary goal of computer vision is to emulate and enhance the human visual system. This field can be broadly categorized into three main types:
- Classification
- Detection
- Segmentation
Classification
Classification, as the term implies, involves determining the category of an object within an image. This can range from simple binary classifications, such as "cat" or "dog," to more complex categories. In the realm of computer vision, each classification output is accompanied by a probability score, reflecting the model's accuracy in identifying the given image. The objective of classification is to allocate the output into distinct categories. If the aim is to categorize a dataset into discrete classes, it is classified as a classification problem.

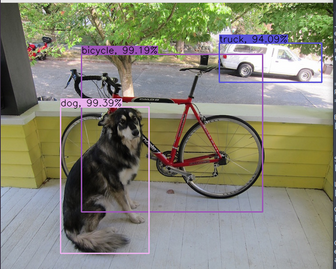
Detection
Detection focuses on pinpointing the location of an object within an image or video. This process begins with classifying which object is present, followed by drawing bounding boxes around the identified objects. Each bounding box comes with a confidence score, allowing a computer vision engineer to filter out boxes based on a specific confidence threshold. The detection process necessitates classification to identify the object before outlining it with a bounding box.
Segmentation
Segmentation involves partitioning an image into various subgroups based on the similarities or differences in pixel characteristics, which aids in identifying objects or setting boundaries within an image. This technique simplifies the analysis of images by reducing their complexity.

Segmentation can be further divided into two categories:
- Semantic Segmentation: Assigns a label to each pixel in the image, treating all instances of a class as one.
- Instance Segmentation: Identifies and localizes distinct objects in an image, treating separate instances of a class as individual entities.
Applications of Computer Vision
Computer vision is widely utilized across various sectors, including:
- Humanoid Robots: For recognizing and interacting with their environment.
- Surveillance and Traffic Cameras: To monitor compliance with traffic regulations and detect violations.
- Drones: For identifying targets in military operations.
- Assembly Lines: To identify and remove defective products through image or video analysis.
- Autonomous Vehicles: To detect other vehicles and surrounding objects.
- Supply Chain Management: Companies like Amazon employ robots equipped with computer vision to accurately pick and deliver packages from warehouses.
