Understanding Data as a Service: Accelerating Your Data Strategy
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Data as a Service
Many are familiar with concepts like IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and SaaS (Software as a Service). But what does it mean to have Data as a Service? Let's explore this concept further.
Definition and Theoretical Framework
Data as a Service (DaaS) represents a data management approach that leverages cloud technology to facilitate the storage, integration, and processing of data through network connections.
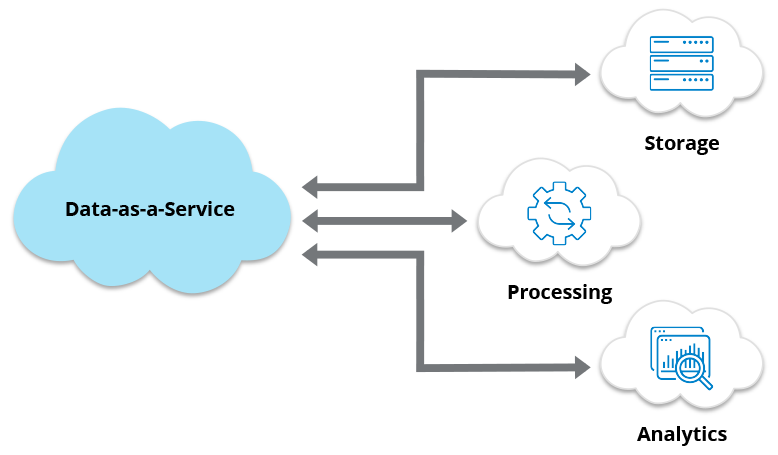
DaaS shares similarities with SaaS, which delivers software applications over the internet, thus eliminating the need for local installations. In the same vein, DaaS externalizes most of the operations related to data storage, integration, and processing.
Instead of relying on self-managed servers or in-house programming to manage data distribution, DaaS enables organizations to transfer data from various source systems—whether on-premises or already cloud-based—directly into the cloud for further distribution.
Benefits of This Innovative Model
Compared to traditional on-premises data storage, DaaS offers several advantages:
- Quick Setup: Organizations can implement DaaS solutions rapidly, allowing for immediate data storage and processing capabilities.
- Reduced Downtime: Cloud infrastructure tends to be less prone to errors, leading to fewer disruptions in DaaS workloads.
- Scalability and Flexibility: DaaS is more adaptable than on-premises solutions, enabling instant resource allocation as needed.
- Cost Management: DaaS platforms automate the management and updates of tools and services, alleviating the need for specialized staff.
Challenges and Potential Issues with DaaS
Despite its benefits, DaaS comes with certain challenges:
- Security Risks: Moving data to a cloud setup and transferring it over networks can create security vulnerabilities absent in on-premises environments. Solutions include using Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs), implementing authentication mechanisms, and ensuring data is stored and transmitted securely.
- Tool Limitations: DaaS platforms may restrict the variety of tools available for data processing, requiring users to work only with those compatible with their service.
- Data Transfer Times: Migrating large volumes of data to a DaaS platform can be time-consuming, especially in areas with limited bandwidth. It's essential for IT departments to assess their network capabilities.
The Future of DaaS
As enterprises increasingly adopt cloud-first strategies, DaaS is becoming a critical component alongside SaaS. With diverse industries and organizations focusing on cloud solutions, it's likely that DaaS will continue to expand its influence in the data management landscape. By simplifying the transfer of data to SaaS-based Data Lakes and Warehouses, companies can allocate more resources toward valuable data analysis activities that drive business growth.
For a deeper understanding of Data as a Service, consider the following resources.
Sources and Further Readings
[1] Hazelcast, Data-as-a-Service (2022)
[2] Talend, What is Data as a Service (2022)
[3] Wikipedia, Data as a Service (2022)
[4] Google, New Google Cloud innovations to unify your data cloud (2022)
Explore the foundational elements of Data as a Service, including its definitions, examples, and benefits.
Gain insights into the introduction of Data as a Service and its significance in modern data management solutions.