The 1E 0102.2–7219 Supernova Mystery Revealed by Hubble
Written on
Chapter 1: The Supernova's Historical Context
In the early 4th century, significant events were unfolding, such as the construction of St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome and Pappus of Alexandria documenting a solar eclipse. During this time, a star erupted in the southern hemisphere, but unfortunately, historical records of this event have not survived. However, the Hubble Space Telescope has recently focused on the remnants of this spectacular explosion, designated as 1E 0102.2–7219. By analyzing the gas and dust surrounding the explosion, astronomers aim to reconstruct the narrative of this ancient cosmic event.
Chapter 2: Observations of the Nebula
The supernova explosion that created this nebula was visible from Earth approximately 1,700 years ago, though it was not identified as such until recently. Located in the Small Magellanic Cloud, a satellite galaxy about 200,000 light-years from our planet, this nebula was initially detected in X-ray wavelengths by NASA’s Einstein Observatory.
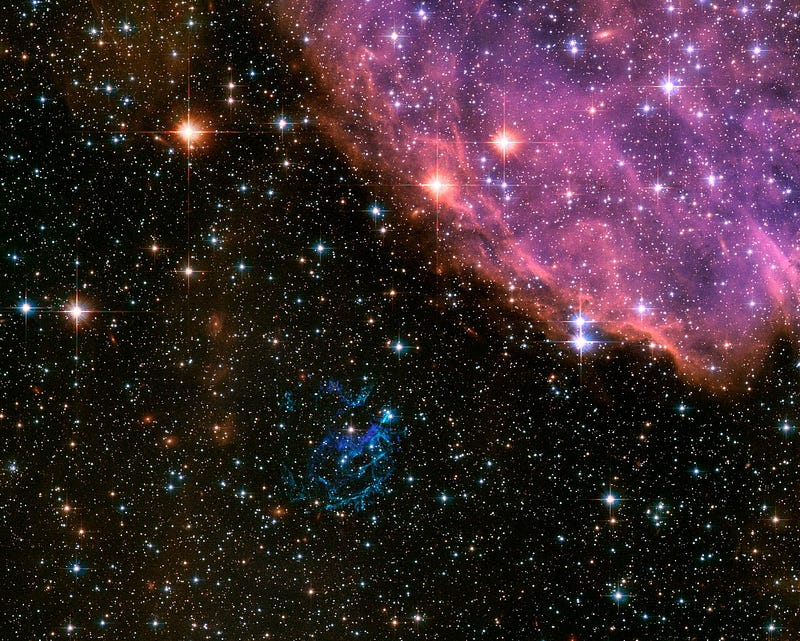

By comparing images taken a decade apart by the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have observed significant changes in the nebula's structure. Different knots within the nebula exhibit varying velocities and trajectories from the explosion's epicenter, averaging speeds of 3.2 million kilometers per hour (almost two million miles per hour). At such speeds, a round trip to the Moon could be completed in just 15 minutes.

Earlier research suggested that the supernova was visible on Earth between 2000 and 1000 years BCE. However, this latest study, which focused on the 22 fastest-moving knots in the nebula, concluded that the explosion actually occurred 1,700 years before our era.
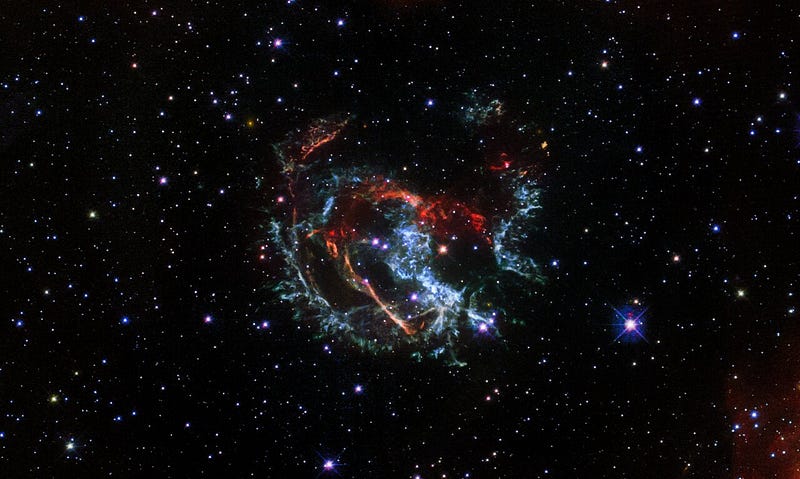

Chapter 3: Tracing the Cosmic Explosion
By analyzing the paths of oxygen-rich, tadpole-shaped clumps in the nebula, astronomers have refined their age estimates of the explosion. Ionized oxygen serves as a useful tracer due to its bright emission in visible light.
The Hubble team reported that the suspected neutron star left by the explosion was detected using the European Southern Observatory’s Very Large Telescope in conjunction with data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory. This neutron star appears to be moving away from the explosion's center at speeds exceeding three million kilometers per hour (1.86 million miles per hour).
The video titled "Hubble Supernova" captures the incredible journey of the Hubble Space Telescope as it investigates the remnants of this ancient supernova, shedding light on its mysteries.
Despite the high speeds, recent studies have raised questions about whether this object is indeed the remnants of the supernova. As John Banovetz from Purdue University noted, "Our research provides a velocity estimate for the candidate neutron star but does not completely resolve the ongoing enigma."
Chapter 4: The Impact of Historical Context
Astronomers discovered that many knots within the nebula had previously collided with material expelled by the star before the explosion, causing some clumps to decelerate and altering earlier assessments.
Danny Milisavljevic of Purdue University emphasized the importance of consistent data comparison: "Previous studies used different cameras on Hubble, but our research utilized the same camera, which allowed for a more accurate comparison over the 10-year span." This highlights the enduring capability of Hubble to provide reliable long-term observations.
In the backdrop of these astronomical discoveries, the Roman Empire was facing turmoil, with civil strife and political upheaval dominating society. It is perhaps fortunate that the "new star" was not visible to those in the northern hemisphere; such an event could have been perceived as an ominous sign, potentially influencing historical trajectories.
James Maynard, the founder and publisher of The Cosmic Companion, resides in Tucson, Arizona, where he enjoys life with his wife, Nicole, and their cat, Max.
Did you enjoy this article? Join us at The Cosmic Companion Network for our podcast, weekly video series, informative newsletters, and news updates on Amazon Alexa and more!